1.6. Fabryka uproszczona (Simple Factory)
1.6.1. Przeznaczenie
Klasa SimpleFactory w poniższym przykładzie jest implementacją wzorca Fabryki uproszczonej.
It differs from the static factory because it is not static. Therefore, you can have multiple factories, differently parameterized, you can subclass it and you can mock it. It always should be preferred over a static factory!
1.6.2. Diagram UML
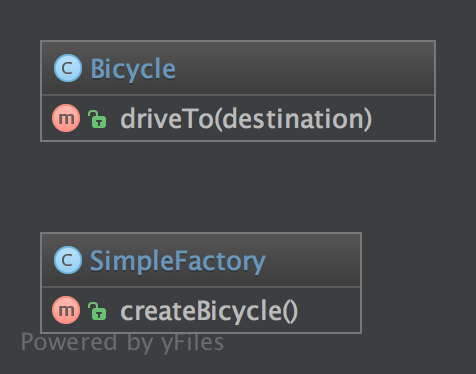
1.6.3. Kod
Ten kod znajdziesz również na GitHub.
SimpleFactory.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\Creational\SimpleFactory;
6
7class SimpleFactory
8{
9 public function createBicycle(): Bicycle
10 {
11 return new Bicycle();
12 }
13}
Bicycle.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\Creational\SimpleFactory;
6
7class Bicycle
8{
9 public function driveTo(string $destination)
10 {
11 }
12}
1.6.4. Usage
1 $factory = new SimpleFactory();
2 $bicycle = $factory->createBicycle();
3 $bicycle->driveTo('Paris');
1.6.5. Testy
Tests/SimpleFactoryTest.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\Creational\SimpleFactory\Tests;
6
7use DesignPatterns\Creational\SimpleFactory\Bicycle;
8use DesignPatterns\Creational\SimpleFactory\SimpleFactory;
9use PHPUnit\Framework\TestCase;
10
11class SimpleFactoryTest extends TestCase
12{
13 public function testCanCreateBicycle()
14 {
15 $bicycle = (new SimpleFactory())->createBicycle();
16 $this->assertInstanceOf(Bicycle::class, $bicycle);
17 }
18}