2.4. Data Mapper
2.4.1. Предназначение
Data Mapper е слой за достъп до данни, който извършва двупосочен трансфер на данни между постоянното хранилище на данни (често релационна база данни) и представяне на данни в паметта (домейн слой). Целта на шаблона е да запази представянето в паметта и постоянното съхранение на данни независимо един от друг и самия картограф (mapper) на данни. Слоят се състои от един или повече картографи (mapper) (или обекти за достъп до данни), извършващи прехвърлянето на данни. Изпълнения на Mapper се различават по обхват. Общите картографи (mappers) ще обработват много различни типове обект на домейн, специалните картографи (mappers) ще работят с един или няколко.
Ключовата точка на този шаблон е, за разлика от Active Record, моделът на данни следва Принципа на единична отговорност.
2.4.2. Примери
DB Object Relational Mapper (ORM): Doctrine2 използва DAO, наречен „EntityRepository“
2.4.3. UML Диаграма
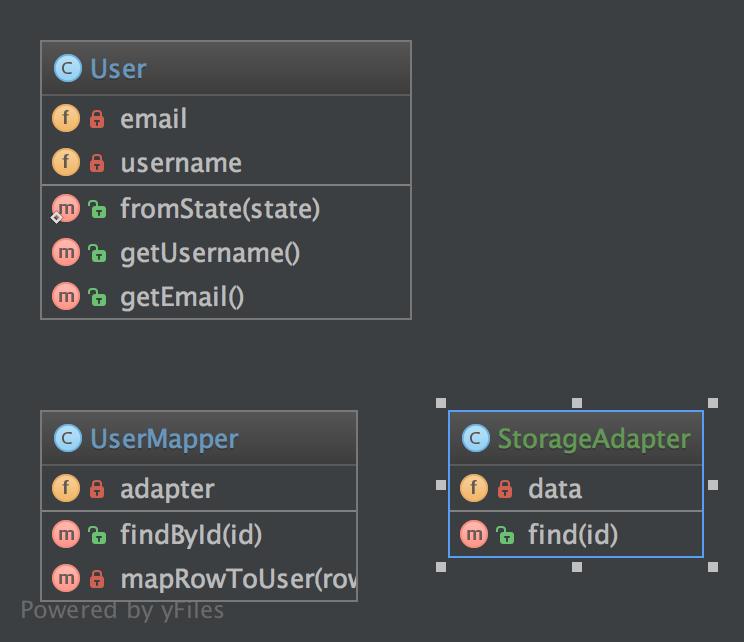
2.4.4. Код
Можете също да намерите този код в GitHub
User.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\Structural\DataMapper;
6
7class User
8{
9 public static function fromState(array $state): User
10 {
11 // validate state before accessing keys!
12
13 return new self(
14 $state['username'],
15 $state['email']
16 );
17 }
18
19 public function __construct(private string $username, private string $email)
20 {
21 }
22
23 public function getUsername(): string
24 {
25 return $this->username;
26 }
27
28 public function getEmail(): string
29 {
30 return $this->email;
31 }
32}
UserMapper.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\Structural\DataMapper;
6
7use InvalidArgumentException;
8
9class UserMapper
10{
11 public function __construct(private StorageAdapter $adapter)
12 {
13 }
14
15 /**
16 * finds a user from storage based on ID and returns a User object located
17 * in memory. Normally this kind of logic will be implemented using the Repository pattern.
18 * However the important part is in mapRowToUser() below, that will create a business object from the
19 * data fetched from storage
20 */
21 public function findById(int $id): User
22 {
23 $result = $this->adapter->find($id);
24
25 if ($result === null) {
26 throw new InvalidArgumentException("User #$id not found");
27 }
28
29 return $this->mapRowToUser($result);
30 }
31
32 private function mapRowToUser(array $row): User
33 {
34 return User::fromState($row);
35 }
36}
StorageAdapter.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\Structural\DataMapper;
6
7class StorageAdapter
8{
9 public function __construct(private array $data)
10 {
11 }
12
13 /**
14 * @return array|null
15 */
16 public function find(int $id)
17 {
18 if (isset($this->data[$id])) {
19 return $this->data[$id];
20 }
21
22 return null;
23 }
24}
2.4.5. Тест
Tests/DataMapperTest.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\Structural\DataMapper\Tests;
6
7use InvalidArgumentException;
8use DesignPatterns\Structural\DataMapper\StorageAdapter;
9use DesignPatterns\Structural\DataMapper\User;
10use DesignPatterns\Structural\DataMapper\UserMapper;
11use PHPUnit\Framework\TestCase;
12
13class DataMapperTest extends TestCase
14{
15 public function testCanMapUserFromStorage()
16 {
17 $storage = new StorageAdapter([1 => ['username' => 'someone', 'email' => 'someone@example.com']]);
18 $mapper = new UserMapper($storage);
19
20 $user = $mapper->findById(1);
21
22 $this->assertInstanceOf(User::class, $user);
23 }
24
25 public function testWillNotMapInvalidData()
26 {
27 $this->expectException(InvalidArgumentException::class);
28
29 $storage = new StorageAdapter([]);
30 $mapper = new UserMapper($storage);
31
32 $mapper->findById(1);
33 }
34}