4.2. Repository (Depo)
4.2.1. Amaç
Etki alanı nesnelerine erişmek için yığın (collection) benzeri bir arayüz kullanarak, etki alanı (domain) ve veri haritalama katmanları (mapping layer) arasında aracılık yapar. Depo, bir veri deposundaki (data store) kalıcı nesnelerin kümesini ve bunların üzerinde gerçekleştirilen işlemleri sarmalayarak (encapsulation), kalıcılık katmanının daha nesne yönelimli bir görünüm almasını sağlar. Depo ayrıca, alan ve veri haritalama katmanları arasında temiz bir ayırma ve tek yönlü bağımlılık (dependency) elde etme amacını destekler.
4.2.2. Örnekler
Doctrine 2 ORM: Varlık (Entity) ve DBAL (Database Abstraction Layer) arasında aracılık yapan ve nesnelere erişmek için yöntemler içeren bir Depo vardır.
Laravel Framework
4.2.3. UML Diyagramı
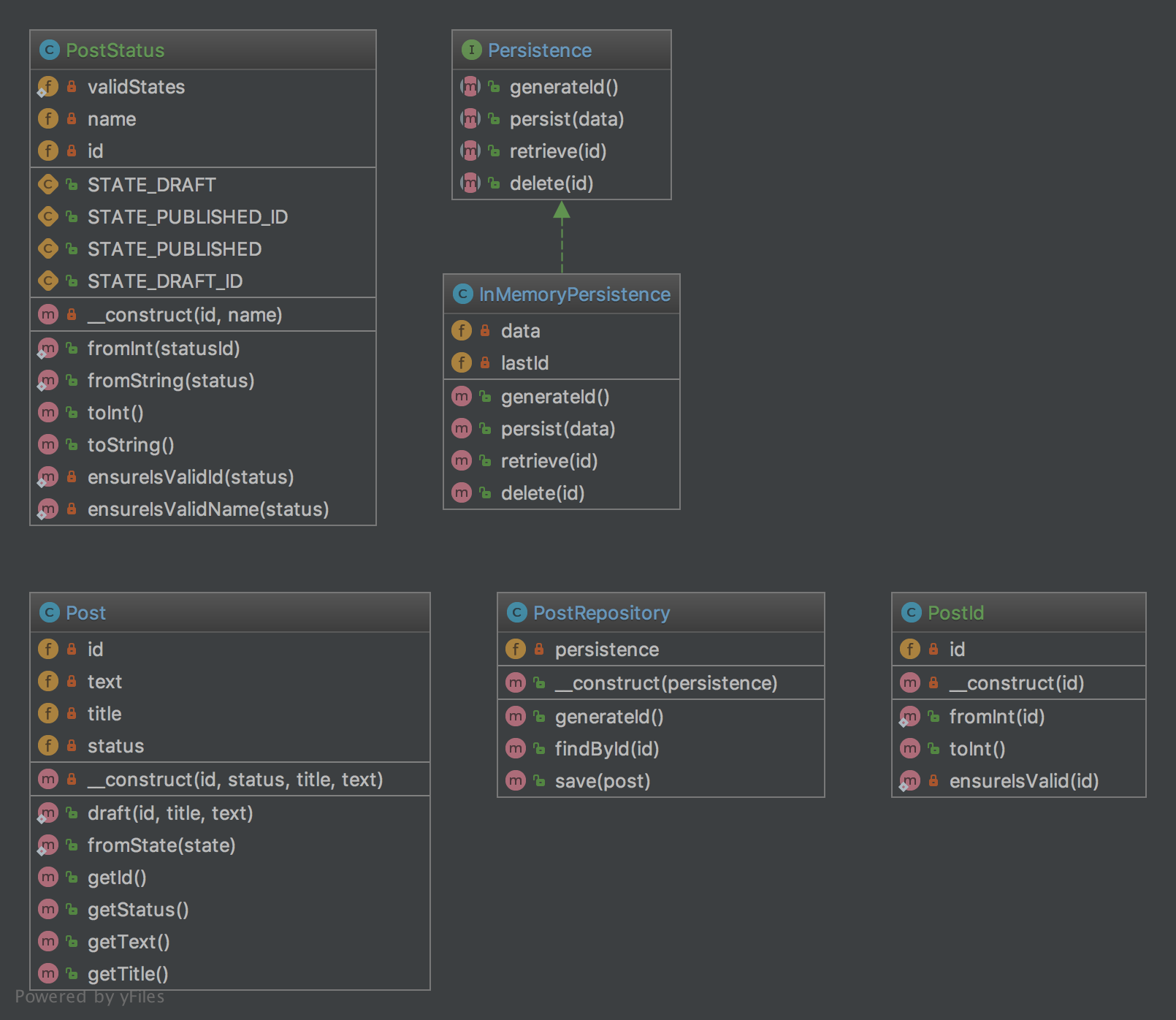
4.2.4. Kod
Bu kodu Github üzerinde de bulabilirsiniz.
Post.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\More\Repository\Domain;
6
7class Post
8{
9 public static function draft(PostId $id, string $title, string $text): Post
10 {
11 return new self(
12 $id,
13 PostStatus::fromString(PostStatus::STATE_DRAFT),
14 $title,
15 $text
16 );
17 }
18
19 public static function fromState(array $state): Post
20 {
21 return new self(
22 PostId::fromInt($state['id']),
23 PostStatus::fromInt($state['statusId']),
24 $state['title'],
25 $state['text']
26 );
27 }
28
29 private function __construct(
30 private PostId $id,
31 private PostStatus $status,
32 private string $title,
33 private string $text
34 ) {
35 }
36
37 public function getId(): PostId
38 {
39 return $this->id;
40 }
41
42 public function getStatus(): PostStatus
43 {
44 return $this->status;
45 }
46
47 public function getText(): string
48 {
49 return $this->text;
50 }
51
52 public function getTitle(): string
53 {
54 return $this->title;
55 }
56}
PostId.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\More\Repository\Domain;
6
7use InvalidArgumentException;
8
9/**
10 * This is a perfect example of a value object that is identifiable by it's value alone and
11 * is guaranteed to be valid each time an instance is created. Another important property of value objects
12 * is immutability.
13 *
14 * Notice also the use of a named constructor (fromInt) which adds a little context when creating an instance.
15 */
16class PostId
17{
18 public static function fromInt(int $id): PostId
19 {
20 self::ensureIsValid($id);
21
22 return new self($id);
23 }
24
25 private function __construct(private int $id)
26 {
27 }
28
29 public function toInt(): int
30 {
31 return $this->id;
32 }
33
34 private static function ensureIsValid(int $id)
35 {
36 if ($id <= 0) {
37 throw new InvalidArgumentException('Invalid PostId given');
38 }
39 }
40}
PostStatus.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\More\Repository\Domain;
6
7use InvalidArgumentException;
8
9/**
10 * Like PostId, this is a value object which holds the value of the current status of a Post. It can be constructed
11 * either from a string or int and is able to validate itself. An instance can then be converted back to int or string.
12 */
13class PostStatus
14{
15 public const STATE_DRAFT_ID = 1;
16 public const STATE_PUBLISHED_ID = 2;
17
18 public const STATE_DRAFT = 'draft';
19 public const STATE_PUBLISHED = 'published';
20
21 private static array $validStates = [
22 self::STATE_DRAFT_ID => self::STATE_DRAFT,
23 self::STATE_PUBLISHED_ID => self::STATE_PUBLISHED,
24 ];
25
26 public static function fromInt(int $statusId)
27 {
28 self::ensureIsValidId($statusId);
29
30 return new self($statusId, self::$validStates[$statusId]);
31 }
32
33 public static function fromString(string $status)
34 {
35 self::ensureIsValidName($status);
36 $state = array_search($status, self::$validStates);
37
38 if ($state === false) {
39 throw new InvalidArgumentException('Invalid state given!');
40 }
41
42 return new self($state, $status);
43 }
44
45 private function __construct(private int $id, private string $name)
46 {
47 }
48
49 public function toInt(): int
50 {
51 return $this->id;
52 }
53
54 /**
55 * there is a reason that I avoid using __toString() as it operates outside of the stack in PHP
56 * and is therefore not able to operate well with exceptions
57 */
58 public function toString(): string
59 {
60 return $this->name;
61 }
62
63 private static function ensureIsValidId(int $status)
64 {
65 if (!in_array($status, array_keys(self::$validStates), true)) {
66 throw new InvalidArgumentException('Invalid status id given');
67 }
68 }
69
70
71 private static function ensureIsValidName(string $status)
72 {
73 if (!in_array($status, self::$validStates, true)) {
74 throw new InvalidArgumentException('Invalid status name given');
75 }
76 }
77}
PostRepository.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\More\Repository;
6
7use OutOfBoundsException;
8use DesignPatterns\More\Repository\Domain\Post;
9use DesignPatterns\More\Repository\Domain\PostId;
10
11/**
12 * This class is situated between Entity layer (class Post) and access object layer (Persistence).
13 *
14 * Repository encapsulates the set of objects persisted in a data store and the operations performed over them
15 * providing a more object-oriented view of the persistence layer
16 *
17 * Repository also supports the objective of achieving a clean separation and one-way dependency
18 * between the domain and data mapping layers
19 */
20class PostRepository
21{
22 public function __construct(private Persistence $persistence)
23 {
24 }
25
26 public function generateId(): PostId
27 {
28 return PostId::fromInt($this->persistence->generateId());
29 }
30
31 public function findById(PostId $id): Post
32 {
33 try {
34 $arrayData = $this->persistence->retrieve($id->toInt());
35 } catch (OutOfBoundsException $e) {
36 throw new OutOfBoundsException(sprintf('Post with id %d does not exist', $id->toInt()), 0, $e);
37 }
38
39 return Post::fromState($arrayData);
40 }
41
42 public function save(Post $post)
43 {
44 $this->persistence->persist([
45 'id' => $post->getId()->toInt(),
46 'statusId' => $post->getStatus()->toInt(),
47 'text' => $post->getText(),
48 'title' => $post->getTitle(),
49 ]);
50 }
51}
Persistence.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\More\Repository;
6
7interface Persistence
8{
9 public function generateId(): int;
10
11 public function persist(array $data);
12
13 public function retrieve(int $id): array;
14
15 public function delete(int $id);
16}
InMemoryPersistence.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\More\Repository;
6
7use OutOfBoundsException;
8
9class InMemoryPersistence implements Persistence
10{
11 private array $data = [];
12 private int $lastId = 0;
13
14 public function generateId(): int
15 {
16 $this->lastId++;
17
18 return $this->lastId;
19 }
20
21 public function persist(array $data)
22 {
23 $this->data[$this->lastId] = $data;
24 }
25
26 public function retrieve(int $id): array
27 {
28 if (!isset($this->data[$id])) {
29 throw new OutOfBoundsException(sprintf('No data found for ID %d', $id));
30 }
31
32 return $this->data[$id];
33 }
34
35 public function delete(int $id)
36 {
37 if (!isset($this->data[$id])) {
38 throw new OutOfBoundsException(sprintf('No data found for ID %d', $id));
39 }
40
41 unset($this->data[$id]);
42 }
43}
4.2.5. Test
Tests/PostRepositoryTest.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\More\Repository\Tests;
6
7use OutOfBoundsException;
8use DesignPatterns\More\Repository\Domain\PostId;
9use DesignPatterns\More\Repository\Domain\PostStatus;
10use DesignPatterns\More\Repository\InMemoryPersistence;
11use DesignPatterns\More\Repository\Domain\Post;
12use DesignPatterns\More\Repository\PostRepository;
13use PHPUnit\Framework\TestCase;
14
15class PostRepositoryTest extends TestCase
16{
17 private PostRepository $repository;
18
19 protected function setUp(): void
20 {
21 $this->repository = new PostRepository(new InMemoryPersistence());
22 }
23
24 public function testCanGenerateId()
25 {
26 $this->assertEquals(1, $this->repository->generateId()->toInt());
27 }
28
29 public function testThrowsExceptionWhenTryingToFindPostWhichDoesNotExist()
30 {
31 $this->expectException(OutOfBoundsException::class);
32 $this->expectExceptionMessage('Post with id 42 does not exist');
33
34 $this->repository->findById(PostId::fromInt(42));
35 }
36
37 public function testCanPersistPostDraft()
38 {
39 $postId = $this->repository->generateId();
40 $post = Post::draft($postId, 'Repository Pattern', 'Design Patterns PHP');
41 $this->repository->save($post);
42
43 $this->repository->findById($postId);
44
45 $this->assertEquals($postId, $this->repository->findById($postId)->getId());
46 $this->assertEquals(PostStatus::STATE_DRAFT, $post->getStatus()->toString());
47 }
48}