2.3. Composite
2.3.1. Purpose
To treat a group of objects the same way as a single instance of the object.
2.3.2. Examples
a form class instance handles all its form elements like a single instance of the form, when
render()is called, it subsequently runs through all its child elements and callsrender()on them
2.3.3. UML Diagram
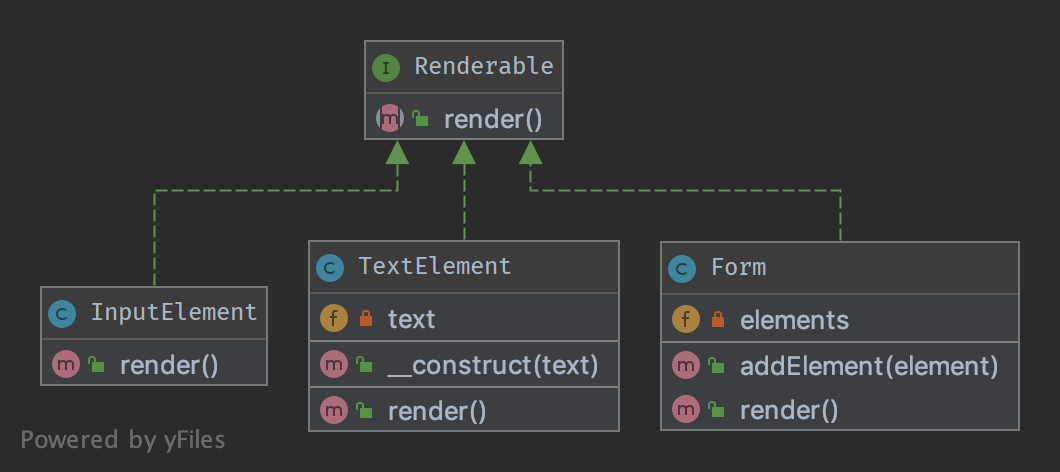
2.3.4. Code
You can also find this code on GitHub
Renderable.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\Structural\Composite;
6
7interface Renderable
8{
9 public function render(): string;
10}
Form.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\Structural\Composite;
6
7/**
8 * The composite node MUST extend the component contract. This is mandatory for building
9 * a tree of components.
10 */
11class Form implements Renderable
12{
13 /**
14 * @var Renderable[]
15 */
16 private array $elements;
17
18 /**
19 * runs through all elements and calls render() on them, then returns the complete representation
20 * of the form.
21 *
22 * from the outside, one will not see this and the form will act like a single object instance
23 */
24 public function render(): string
25 {
26 $formCode = '<form>';
27
28 foreach ($this->elements as $element) {
29 $formCode .= $element->render();
30 }
31
32 return $formCode . '</form>';
33 }
34
35 public function addElement(Renderable $element)
36 {
37 $this->elements[] = $element;
38 }
39}
InputElement.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\Structural\Composite;
6
7class InputElement implements Renderable
8{
9 public function render(): string
10 {
11 return '<input type="text" />';
12 }
13}
TextElement.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\Structural\Composite;
6
7class TextElement implements Renderable
8{
9 public function __construct(private string $text)
10 {
11 }
12
13 public function render(): string
14 {
15 return $this->text;
16 }
17}
2.3.5. Test
Tests/CompositeTest.php
1<?php
2
3declare(strict_types=1);
4
5namespace DesignPatterns\Structural\Composite\Tests;
6
7use DesignPatterns\Structural\Composite\Form;
8use DesignPatterns\Structural\Composite\TextElement;
9use DesignPatterns\Structural\Composite\InputElement;
10use PHPUnit\Framework\TestCase;
11
12class CompositeTest extends TestCase
13{
14 public function testRender()
15 {
16 $form = new Form();
17 $form->addElement(new TextElement('Email:'));
18 $form->addElement(new InputElement());
19 $embed = new Form();
20 $embed->addElement(new TextElement('Password:'));
21 $embed->addElement(new InputElement());
22 $form->addElement($embed);
23
24 // This is just an example, in a real world scenario it is important to remember that web browsers do not
25 // currently support nested forms
26
27 $this->assertSame(
28 '<form>Email:<input type="text" /><form>Password:<input type="text" /></form></form>',
29 $form->render()
30 );
31 }
32}